The Model Gateway section in Axoma is a centralized interface that enables Super Admins to handle all aspects of integrating
and controlling Large Language Model (LLM) services within the platform. This area is designed for flexibility, security, and scalability, giving organizations full administrative control over how LLMs are accessed, configured, and budgeted across different applications and environments.
Home > Settings > AI Platform > Model Gateway
Important: Once the API key is generated, make sure to copy or download it and store it in a secure location.
This key will be required for future use and cannot be retrieved again from the platform.
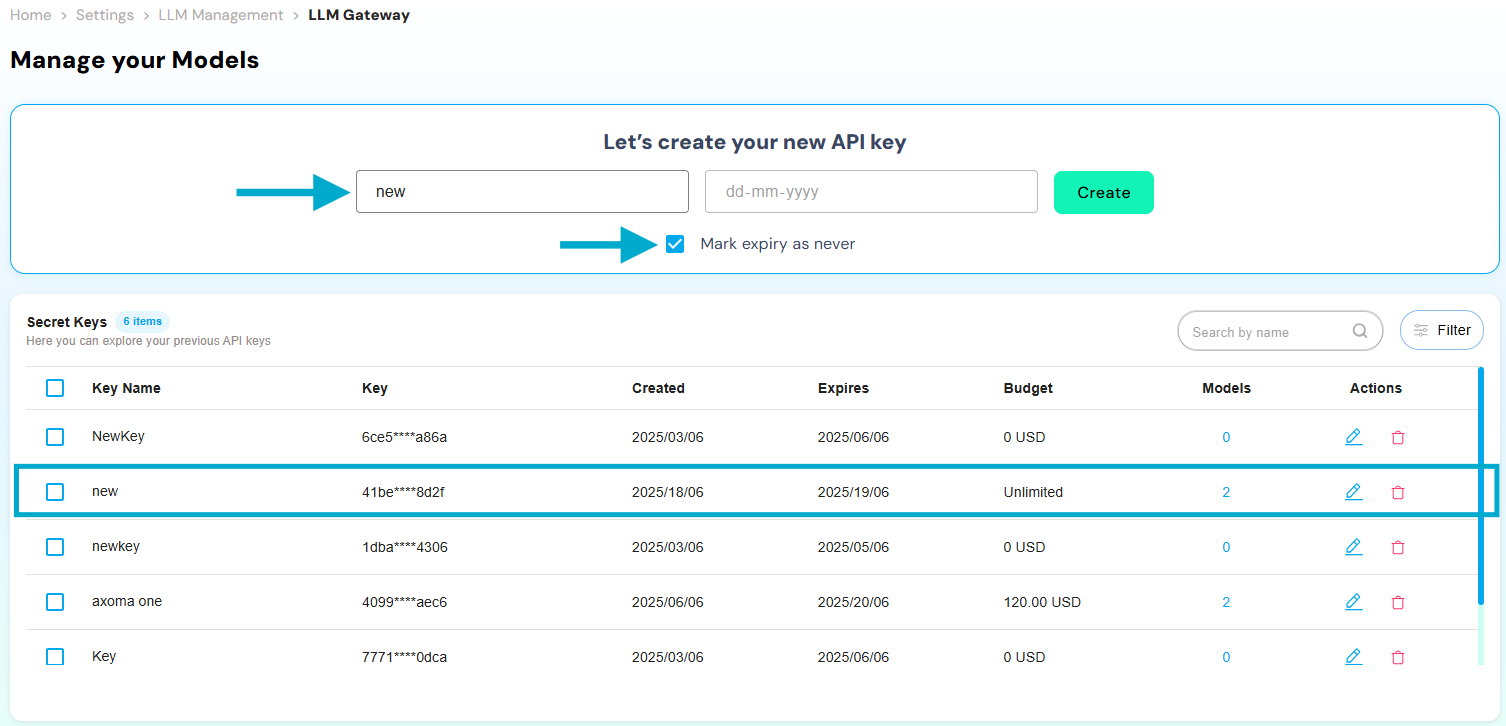
API Key Creation
Administrators can generate secure API keys that act as gateways to connect the platform with third-party LLM providers.
These keys are essential for authenticating model requests and maintaining control over access.
Within Global Settings > LLM Management, a Super Admin can:
- Generate an API Key
- Set an Expiry Date (must be later than the current date) can choose Never Expiring date option.
- Add/Update LLMs and Embedding Models from supported providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Amazon,
or organization-specific models against the generated key.
- Configure Model Parameters and Budgets including token limits, temperature, max tokens, and usage permissions
- Save configurations under the associated API key.
Once saved, the API key enables seamless interaction across models via a unified access point, simplifying integration
and supporting multi-model orchestration.